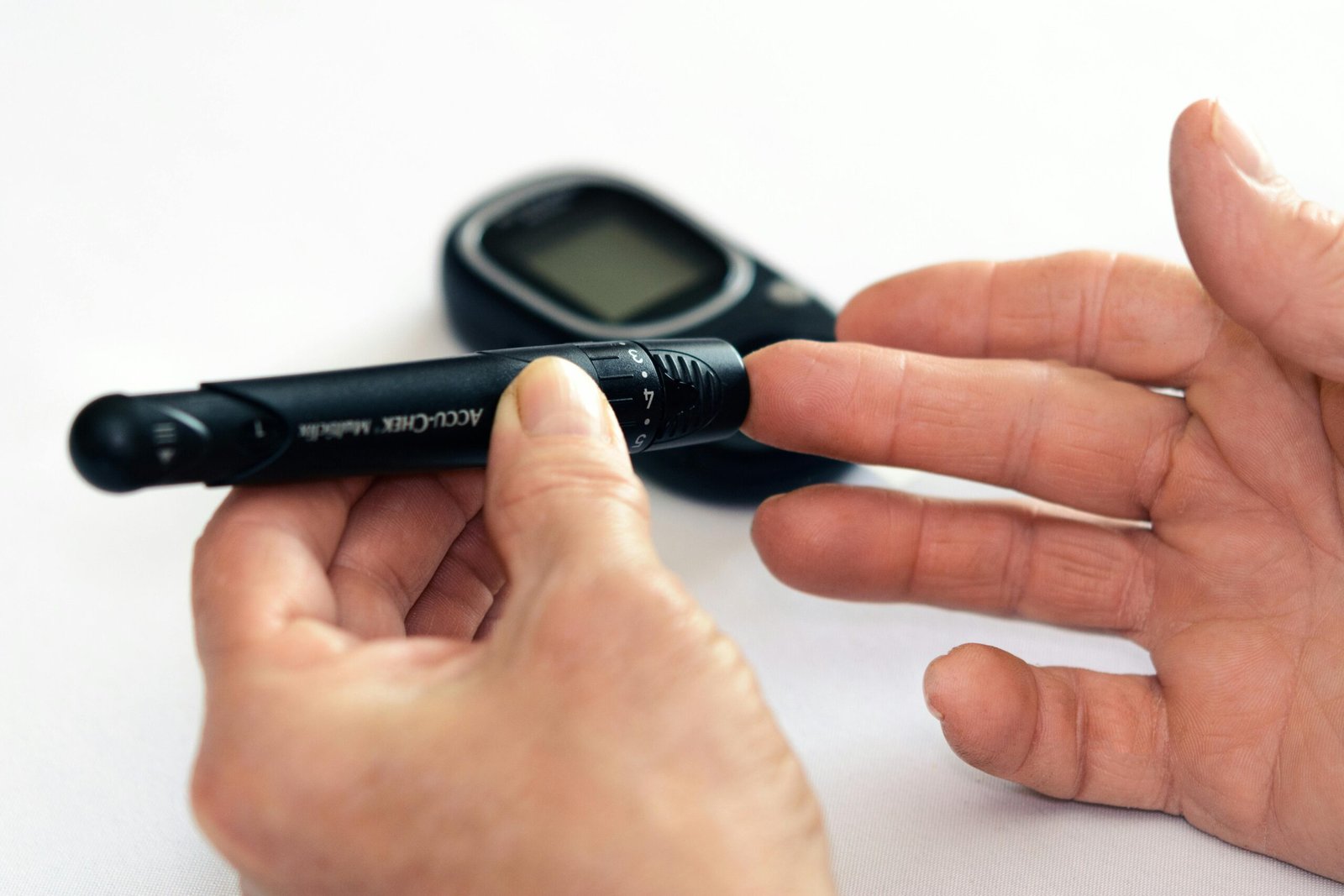
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the body’s ability to control the blood sugar level. It is a state in which the primary energy source, glucose, cannot easily be utilized by cells. The principal source behind elevated blood glucose levels is a hormone called insulin that is produced by the pancreas. Diabetics lack sufficient insulin or cannot utilize the insulin synthesized and hence have increased sugar levels in the body which can cause serious health problems in the long run.
Diabetes Types:
Diabetes type 1:
This Is an autoimmune disorder whereby the oons body immune attacks the pancreas cells that produce insulin.
Insulin is required in children with type 1 diabetes especially for those who tend to not produce insulin by themselves.
It can develop in adults too, however in most cases it occurs in childhood or early teenage.
Diabetes type 2:
This is the most common form of diabetes that is also associated with insulin insensitivity. Insulin is still generated by the body, but it is not utilized properly.
It is more common in adults but given sedentary behavior and the challenges around food, younger populations are also starting to see a rise in type 2 diabetes.
Insulin or medication is sometimes required, yet diabetes type 2 is commonly managed through diet. Exercises and other lifestyle changes can also assist people with this kind of lifestyle illness.
Gestational diabetes:
is when the body does not respond well to insulin during pregnancy, resulting in this condition.
Both the mother and the child are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future thanks to this condition.
Prediabetes:
this is when blood sugar levels are less severe than those of an adult but still above the normal levels.
If someone has pre-diabetes and doesn’t make changes in their diet and activities, that person’s chances of getting type 2 diabetes are extremely high.
Symptoms of diabetes include:
Excess urination
Increased thirst
Unintentional Body weight loss
Weakness
Blurred eyesight
Constant sores and infections that take a long time to resolve.
Causative Factors and Risks:
Type 1 diabetes: Its exact cause is unknown, but it’s generally accepted that its appearance is the consequence of both environmental and genetic factors.
The risk factors for type 2 diabetes mellitus include being overweight, lack of physical activity, eating a poor diet, having a family history of diabetes, and advancing age. If you are overweight, especially around the abdomen, you are more likely to develop insulin resistance too.
Gestational Diabetes: This condition is due to pregnancy hormones and previously existing risk factors like genetics and obesity.
Complications of Diabetes: If diabetes is left untreated or uncontrolled, there will be some very high-risk complications that may ensue.
Cardiovascular disease: There is a higher susceptibility to high blood pressure enhanced risk of heart diseases and stroke.
Neuropathy: High blood sugar levels can lead to nerve damage which causes pain, numbness or tingling sensations in the extremities especially in the feet and legs.
Nephropathy, or kidney damage: Diabetes may end up destroying the kidney filtration’s functionality and this may eventually lead to renal dysfunction.
Diabetes can also lead to Retinopathy which pertains to retinal cavity damage that occurs due to blood vessels seepage and may end up leading to blindness or any other eye defect.
Foot problems: Impaired blood flow and damaged nerves may lead to severe bacterial infection and in severe cases learning amputation might be necessary.
Skin diseases: Such disorders include infections following the increased susceptibility to skin diseases.
The diagnosis is:
Fasting Blood Sugar Test: Taking blood sugar count in the morning after an overnight fasting period shows how strong is diabetic condition. Fasting blood glucose counts of more than 126mg/dl show that the person has diabetes.
Blood glucose levels are claimed to have been achieved within a span of approximately two to three months and an A1C test presents one such level. Diabetes is diagnosed if A1C is equal to 6.5% and above.
The oral glucose tolerance test predetermines various glucose-related measurement points between fasting durations and the 2-hour mark when carbohydrates in the form of a glucose-sweetened drink are consumed. Diabetes is defined as a two ساعت زخم است که 200 mg/dL or more levels are elevated than the standard.
Treatment and Management:
Changes in Lifestyle:
Diet: By maintaining a healthy diet that includes sufficient fruits, vegetables, lean meat Protein, whole grain cereals, and healthy fats, blood sugar levels can efficiently be managed. Reducing consumption of processed carbohydrates and sugar should also be a priority.
Exercise: Consistent physical activity effectively leads to lower blood sugar concentrations and enhanced insulin utilization in the body.
Weight management is crucial especially for those with type 2 diabetes or are prone to developing the condition.
Drugs:
Among the people with type 1 diabetes and some with type 2 diabetes, insulin is necessary. Helps to manage blood glucose concentration.
Oral Drugs: Drugs commonly called metformin, sulfonylureas, etc. are helpful in improving the insulin sensitivity and blood sugar levels of patients with type 2 diabetes.
GLP-1 Agonists: Hunger suppression drugs, blood glucose regulation drugs, and weight loss support Steroids.
SGLT-2 Inhibitors: Help the kidneys to excrete excess glucose into the urine from the blood vessels.
Blood Sugar level:
For good diabetes management, blood sugar levels need to be checked regularly as target levels are required.
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and blood glucose meters are very common tools used in this.
Prevention:
Type 1 Diabetes: It is not possible to avoid the type 1 diabetes as far as now.
Type 2 Diabetes: Moderate risk factors for type 2 diabetes can be practically eradicated by practicing healthy lifestyle with proper diet, exercise, normal weight and cessation of smoking.
Risk for gestational diabetes can be reduced through appropriate diet and regular exercise before and during the pregnancy.
To summarize the complexities of the pleasant disease, it should be noted that it is a progressive disease process which is chronic in nature and needs lifelong control. Nevertheless, people with diabetes can enjoy active and fruitful lives with the right combination of medical and lifestyle interventions. Such risk factors are avoided and health is preserved through appropriate treatment, regular follow up and early detection.


0 Comments